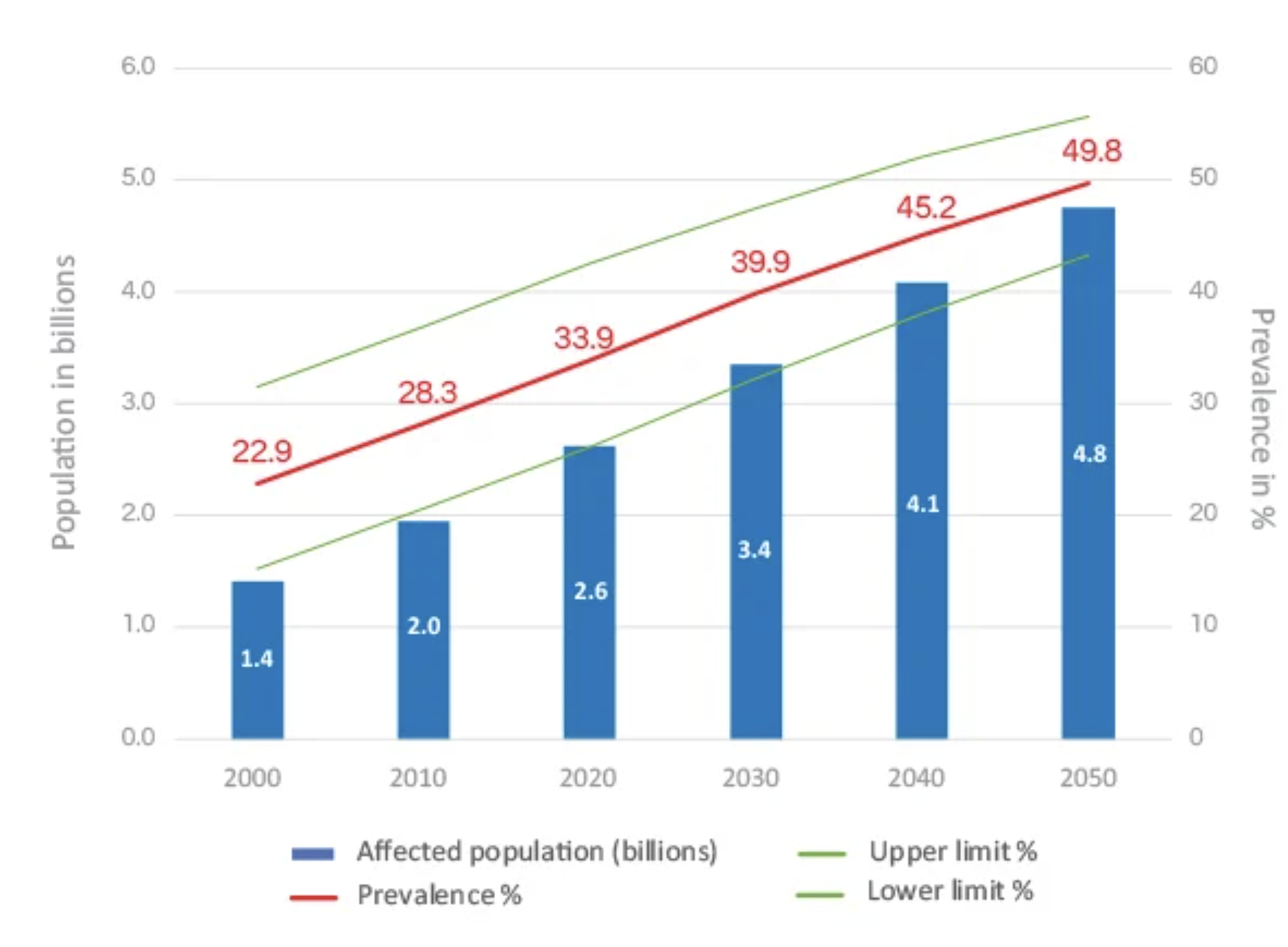
world myopia population increases 0.6 billion people or prevalence 5% every 10 years.
Based on international myopia institute, RISING PREVALENCE OF MYOPIA: 2010 TO 2050
https://myopiainstitute.org/myopia/
Evidence is mounting that myopia is growing around the world, with a recent study estimating that on average, 30% of the world is currently myopic and by 2050, almost 50% will be myopic, that’s a staggering 5 billion people.
The hot spots of myopia are East and South East Asia where countries such as South Korea, Taiwan, Singapore, China and Japan have a prevalence of myopia of 80 to 90 %.
But myopia prevalence is rising and the USA has reported a prevalence of 42%, almost doubling in three decades.
But genetic changes happen slowly, so they can’t explain the rapid rises.
On NetMagazine of American Academy of Ophthalmology, Myopia Research: From the Margins to the Mainstream.
https://www.aao.org/eyenet/article/myopia-research-from-margins-to-mainstream
There are certainly individuals with a genetic propensity for myopia, said Prof. Congdon.
“But genetic changes happen slowly, so they can’t explain the rapid rises we’re experiencing.”
Where prevalence is particularly high, such as in Hong Kong or Taiwan,
most would agree that a combination of genetics and environmental factors are contributing, he said.
since genetic factor should cause myopia rate is stable or slowly, the rapid rising is not related to genetic factor.
the other factor is environmental factor, so environmental factor is related to rapid increase rate of myopia.
What dominates in environmental factor inducing rapid increase of myopia?
Based on research published on the lancet,Association between digital smart device use and myopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Smart device screen time alone or in combination with computer use was significantly associated with myopia.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/landig/article/PIIS2589-7500(21)00135-7/fulltext
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8374145/
What is in smart device screen or computer? Flicker
In the research paper: Impact of Temporal Visual Flicker on Spatial Contrast Sensitivity in Myopia
Our data suggest that exposure to perceivable high-frequency flicker enhances important aspects of spatial contrast sensitivity, and these enhancements are correlated to the degree of myopia.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8374145/
iPhone2 photo of laptop computer
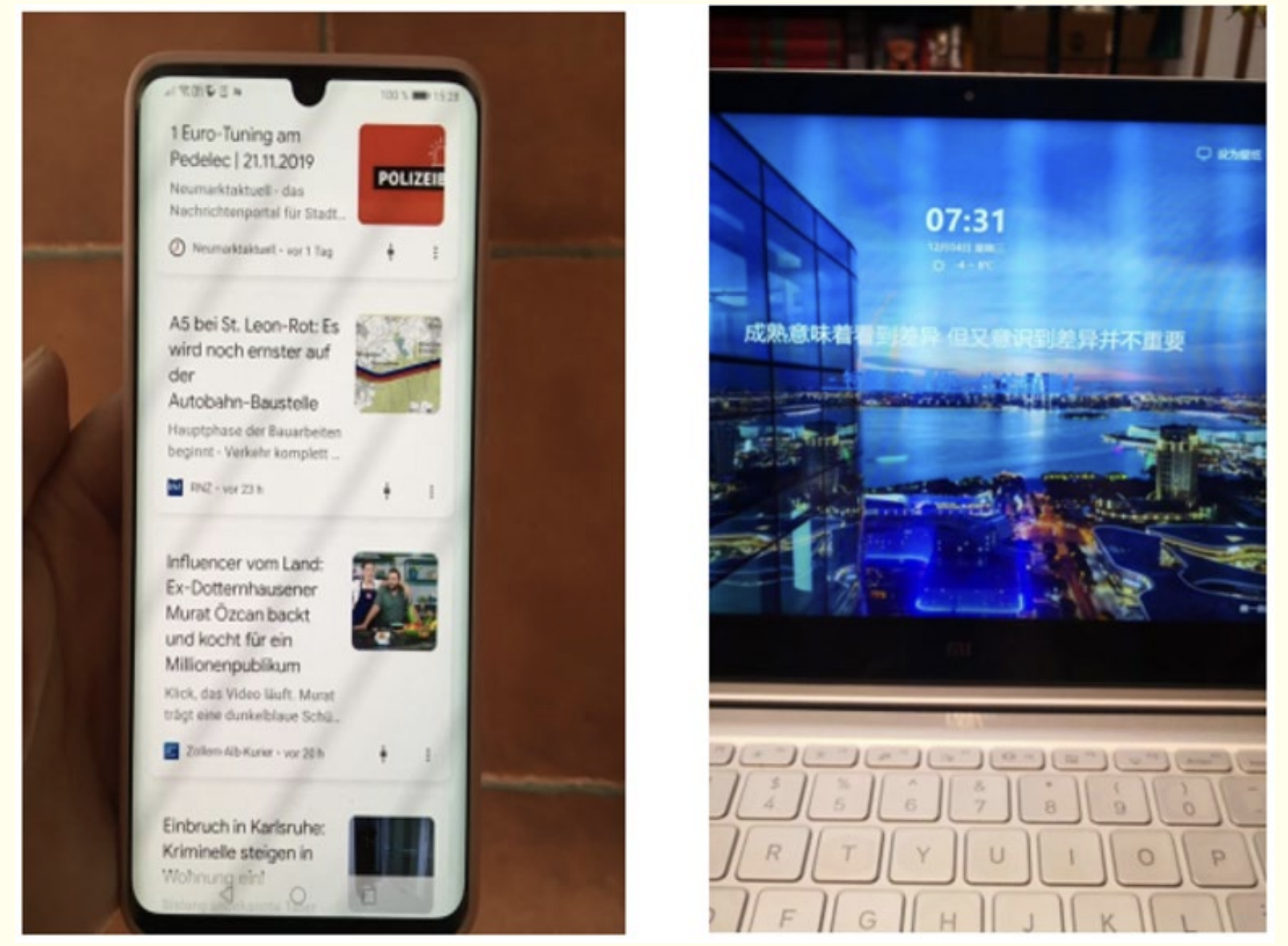
on the left, the stripes showed flicker on a smart phone; on the right, the stripes showed flicker on a laptop computer.
iPhone2 photo of lamps
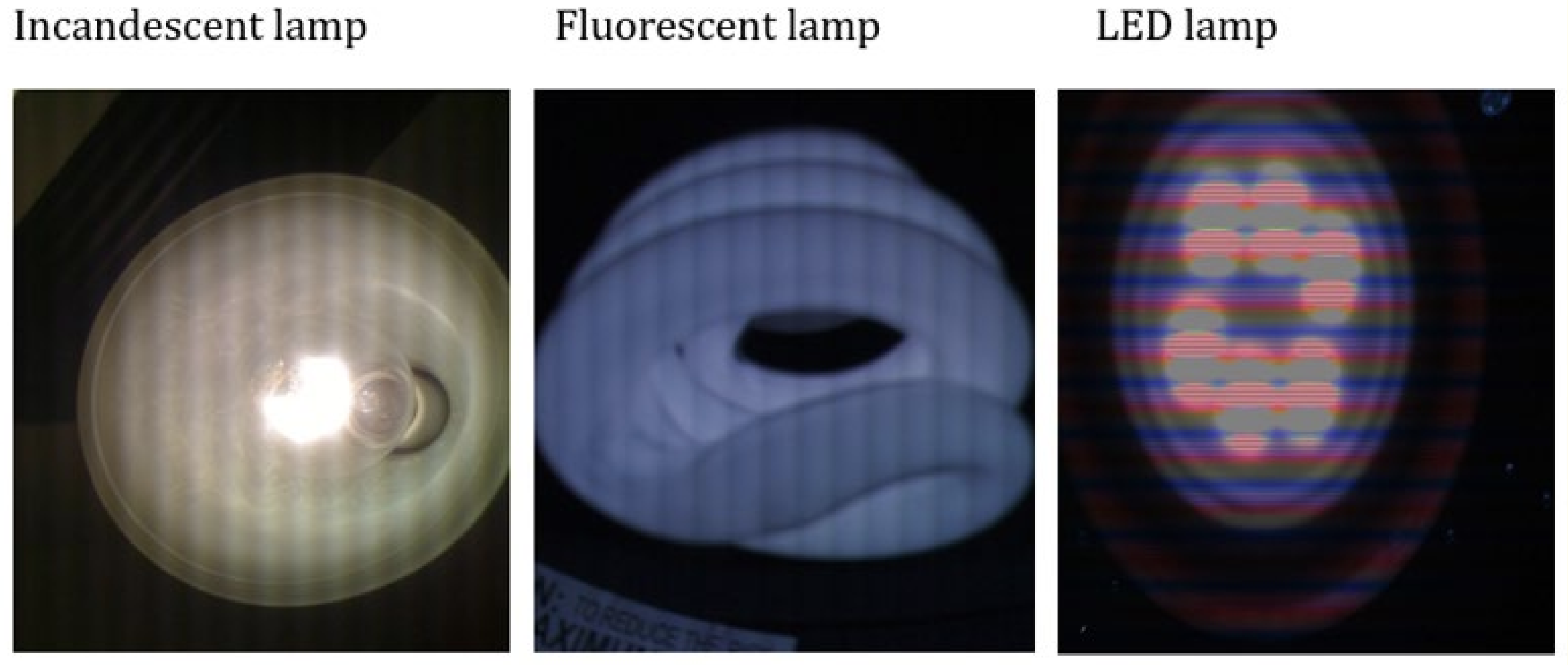
the stripes of the photo are the flicker light of different lamps: an incandescent lamp, a fluorescent lamp and a LED lamp
Research on flicker light impact
Hospital of Nantong University in China found myopia can be induced by low frequency "flicker light" in B6 mice. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21273796/
La Trobe University in Anstralia found low frequency temporal modulation of light promotes a myopic shift. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16579985/
Fu Dan university in China did research and drew conclusion: Myopia can be induced by 0.5-Hz FL in guinea pigs at puberty. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5620382/
pupil constricted in bright light and dilated in dim light

the size of the pupil corresponds to the average light intensity. If light intensity is too strong, the pupil will constrict to avoid intense light hurt on retina
Flicker is a human-visible change in luminance of an illuminated surface or light source which can be due to fluctuations of the light source itself.
flicker is varying illumination light will cause pupils constricted and dilated.
Pupil size increased with illumination decrements.
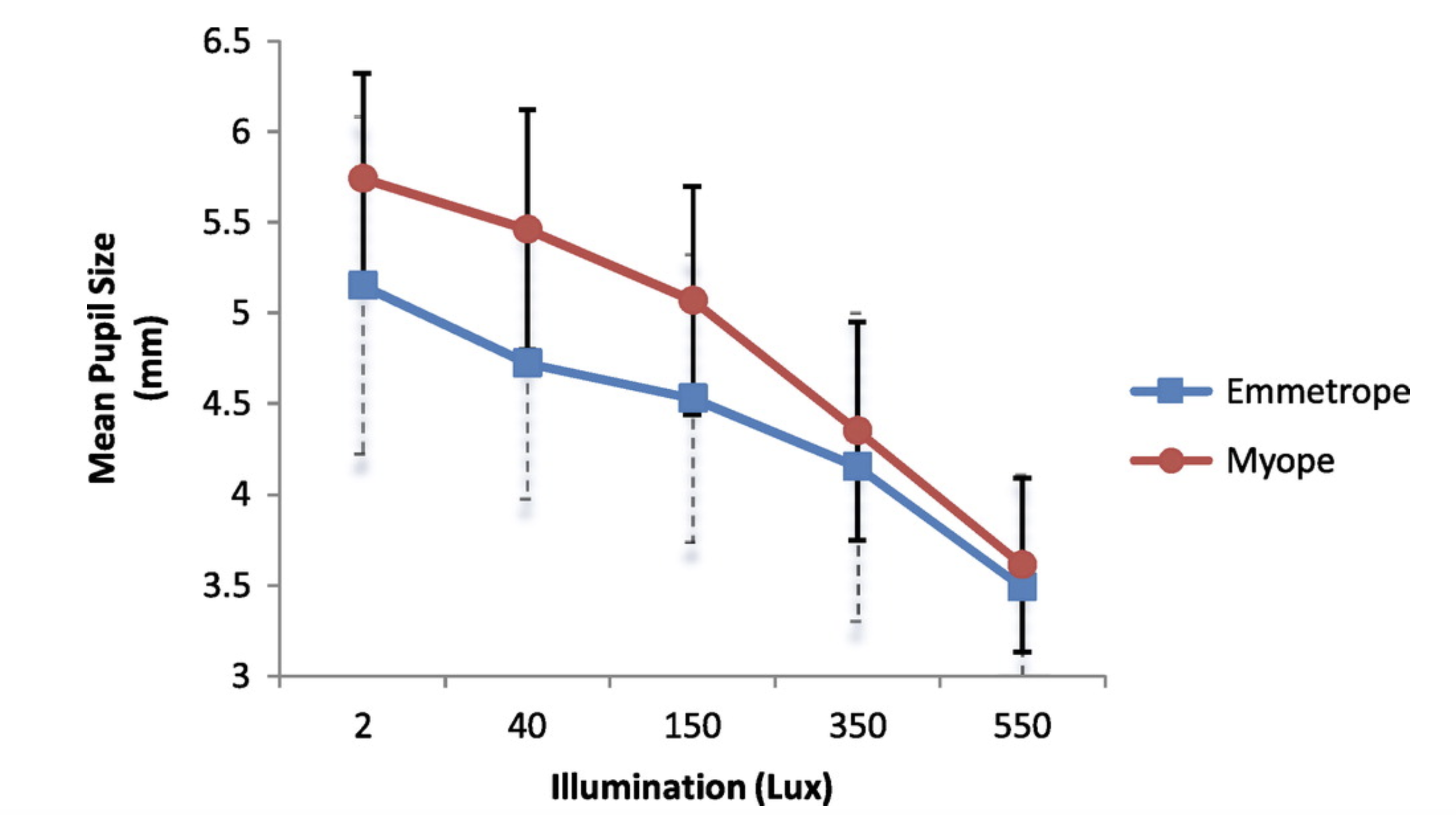
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/2331205X.2017.1338824
The size of the pupil is determined by illumination of the light
Pupil size measurements were performed with room lights at 2, 40, 150, 350 and 550 lux. All light levels were measured with the Visante™ OCT internal fixation light on. Two or three light levels per day were done per subject until all 5 levels were completed. Subjects were given a combined illumination adaptation and relaxation period of 30 min between light level changes. The experiment was performed in a white walled room with no windows that is usually used for eye examination. Lighting source was from ceiling mounted tungsten light with in-wall dimmer control that can render the room into total darkness or very brightly lit.
The flicker light will have varying illumination that will result in pupil size changing frequently.
pupil size is bigger and lens shape is thinner; pupil size is smaller and lens shape is thicker
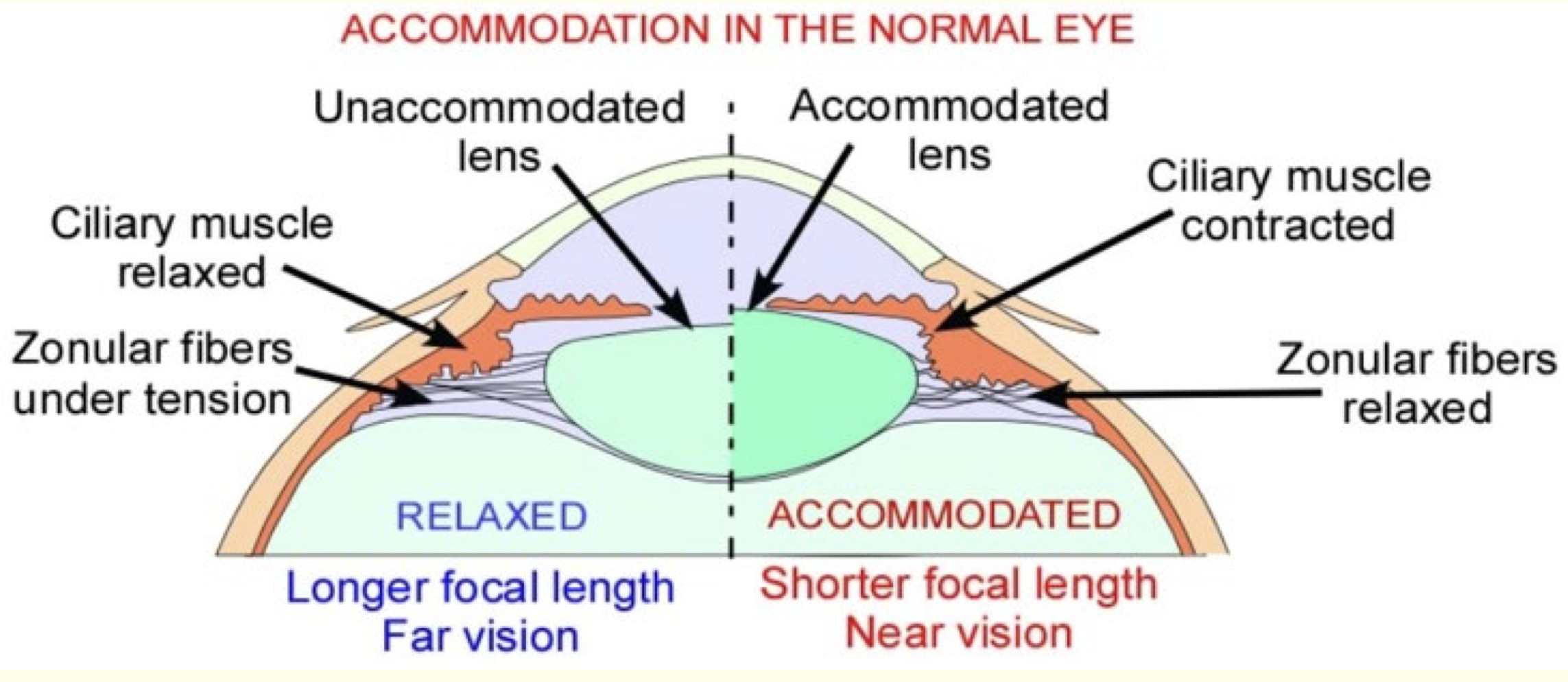
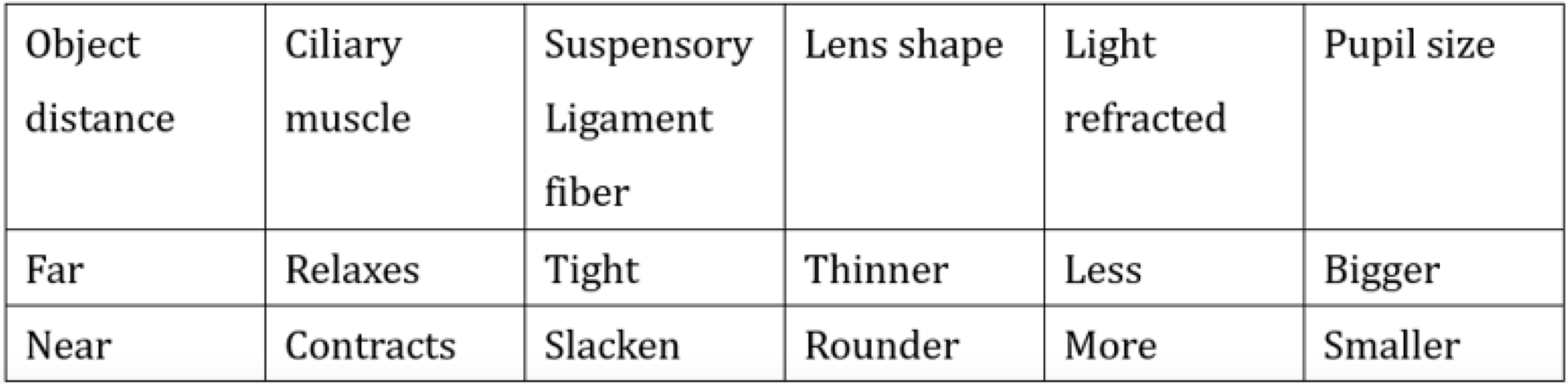
As above, when the light is brighter, the illumination is higher, pupils size is smaller and the lens shape is thicker
As above, when the light is darker, the illumination is lower, pupils size is bigger and the lens shape is thinner
The flicker changes the light from bright to dark frequently, the lens shape is changing from thicker to thinner frequently, the Ciliary muscle will lose flexibility to control lens shape
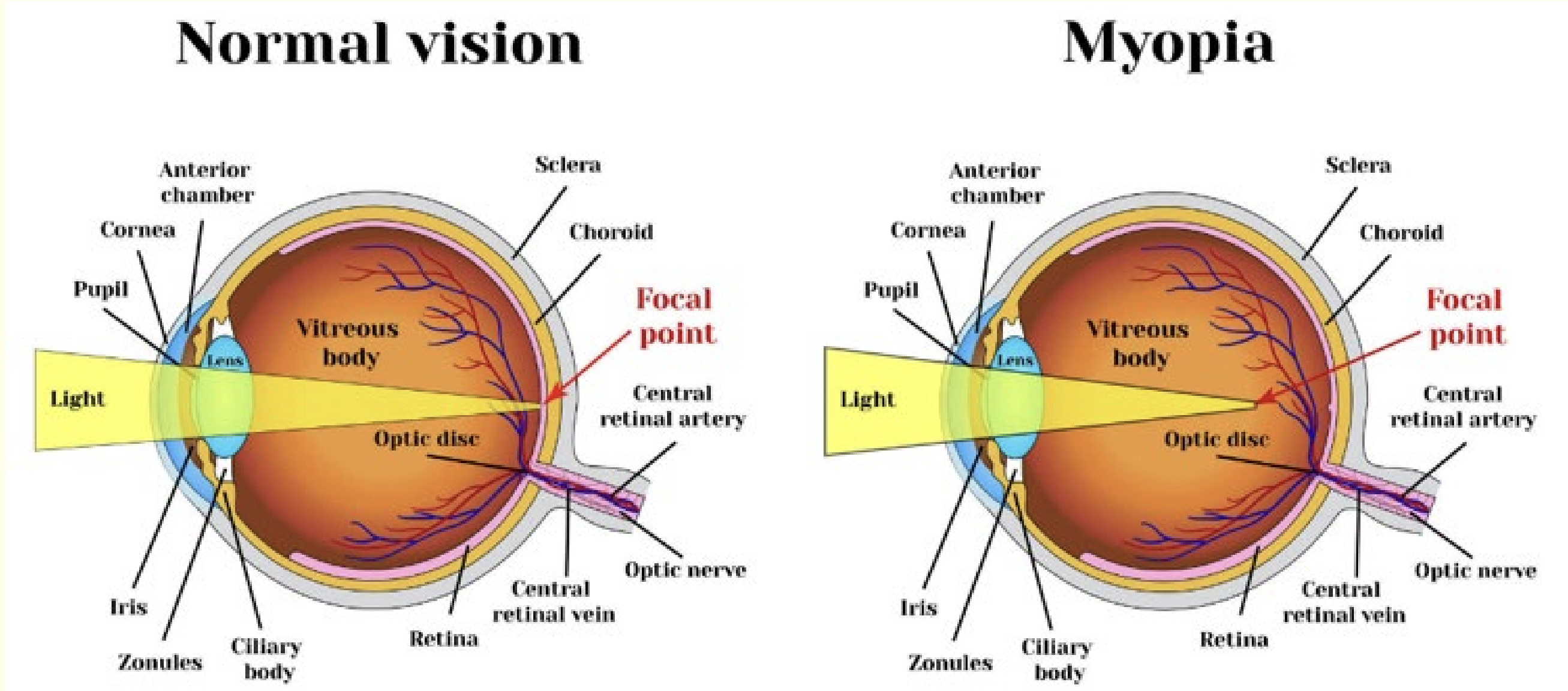
Myopia is characterized by the inability of ciliary muscles to relax and thin out the lens when seeing distant objects. Chronically tense ciliary muscles cause the focal point of light to be too far in front of the retina rather than focusing directly on it, which results in blurry vision
Eye structure with normal vision vs myopia
First step: Pseudomyopia
Pseudo myopia refers to an intermittent and temporary shift in refractive error of the eye towards myopia, in which the focusing of light in front of the retina is due to a transient spasm of the ciliary muscle causing an increase in the refractive power of the eye.
Second step: Permanent myopia
If eyes strain and ocular fatigue are reduced during the stage of pseudo myopia, eyesight may return to normal. However, if the ciliary muscles continue to stay chronically contracted, pseudomyopia can progress into permanent myopia.Potentially poor contractility, of ciliary muscle which may result in the development and progression of myopia.
The ciliary contraction without relax is the root cause of myopia
constant exposure to flicker causes the ciliary muscles to stay in a tense position for long periods of time, which reduces their elasticity and renders them unable to adjust lenses to focus on faraway objects.
St Erik’s Eye Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden found Asthenopia (eyestrain) is significantly associated with uncorrected visual acuity and with myopia
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18484506/